Hw4
Fake News?
In this blog post, I will develop and asses a fake news classifier
Imports
import nltk
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import re
import string
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import losses
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing import TextVectorization
from tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing import StringLookup
from tensorflow.keras import utils
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import plotly.express as px
import plotly.io as pio
pio.templates.default = "plotly_white"
Read in the data
train_url = "https://github.com/PhilChodrow/PIC16b/blob/master/datasets/fake_news_train.csv?raw=true"
df = pd.read_csv(train_url)
mydata=df
Making a data set
After reading in the data, I created a function that removes stop words (as, the, of, etc.) using nltk.corpus. The function also returns a dataset with title and text of an article as the inputs and fake as the output.
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
stop = stopwords.words('english')
def make_dataset(inpdata):
inpdata["title"] = inpdata["title"].apply(lambda x: ' '.join([word for word in x.split() if word not in (stop)])) #removing stop words from titles
inpdata['text'] = inpdata['text'].apply(lambda x: ' '.join([word for word in x.split() if word not in (stop)])) #removing stop words from the texts
data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
( # dictionary for input data/features
{ "title": inpdata[["title"]],
"text": inpdata[["text"]]
},
# dictionary for output data/labels
{ "fake": inpdata["fake"] #single brackets will return one column, two brackets will return a full df
}
)
)
return data.batch(100) #batch the dataset
Train and Validation
Then I split 20% of the dataset I made to use for validation.
mydata = make_dataset(mydata)
mydata = mydata.shuffle(buffer_size = len(mydata))
train_size = int(0.8*len(mydata)) #80% train
val_size = int(0.2*len(mydata)) #20% validation
train = mydata.take(train_size)
val = mydata.skip(train_size).take(val_size)
Base Rate
In order to determine the base rate, I start by creating an iterator to evaluate the labels on the training data
labels_iterator= train.unbatch().map(lambda dict_title_text, label: label).as_numpy_iterator()
Then I create two integers. Depending on the value in the label, fake, one of these integer variables will increase. This keeps track of how many fake and real articles there are. This will be used to determine the accuracy of the model (the base rate).
first_num = 0 #create an int
sec_num = 0 #create an int
for i in labels_iterator:
if i["fake"]==0: #if its not fake, increase the value of the first int
first_num+=1
else: #if its fake, increase the value of the second int
sec_num+=1
The base rate is approximately 10%. If every news was identified as fake, it would be about 10% accurate.
Text Vectorization
#preparing a text vectorization layer for tf model
size_vocabulary = 2000
def standardization(input_data):
lowercase = tf.strings.lower(input_data)
no_punctuation = tf.strings.regex_replace(lowercase,
'[%s]' % re.escape(string.punctuation),'')
return no_punctuation
title_vectorize_layer = TextVectorization(
standardize=standardization,
max_tokens=size_vocabulary, # only consider this many words
output_mode='int',
output_sequence_length=500)
title_vectorize_layer.adapt(train.map(lambda x, y: x["title"]))
First Model - Using article titles to detect fake news
To start my first model, I defined the inputs. This model will just take the article title as input.
# inputs
titles_input = keras.Input(
shape = (1,),
name = "title",
dtype = "string"
)
Next, I created the layers needed for processing the titles
titles_features = title_vectorize_layer(titles_input)
## Add embedding layer , dropout ...
titles_features = title_vectorize_layer(titles_input) # apply this "function TextVectorization layer" to lyrics_input
titles_features = layers.Embedding(size_vocabulary, output_dim = 2, name = "embedding")(titles_features) #need to give name embedding to reference layer
titles_features = layers.Dropout(0.2)(titles_features)
titles_features = layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()(titles_features)
titles_features = layers.Dropout(0.2)(titles_features)
titles_features = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(titles_features)
I created an output layer
output = layers.Dense(2, name = "fake")(titles_features)
Defined the model
model1 = keras.Model(
inputs = titles_input,
outputs = output
)
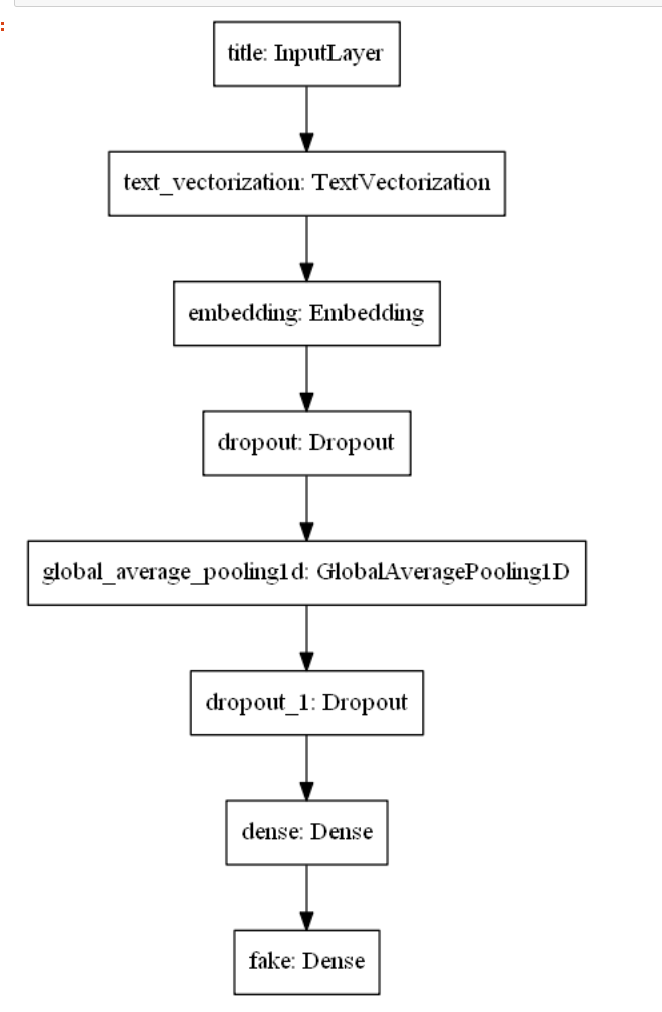
Visualized the model
keras.utils.plot_model(model1)
Compile the model
model1.compile(optimizer="adam",
loss = losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"])
Fit the model
history = model1.fit(train,
validation_data=val,
epochs = 20,
verbose = False)
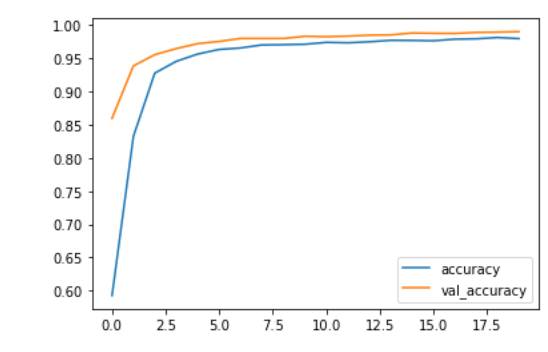
Create a plot to visualize the model’s accuracy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history["accuracy"])
plt.plot(history.history["val_accuracy"])
Model 2 - Using article text to detect fake news
I followed the same steps as the first model, but I examine titles instead of text
Text Vectorization
text_vectorize_layer = TextVectorization(
standardize=standardization,
max_tokens=size_vocabulary, # only consider this many words
output_mode='int',
output_sequence_length=500)
text_vectorize_layer.adapt(train.map(lambda x, y: x["text"]))
Inputs
text_input = keras.Input(
shape = (1,),
name = "text",
dtype = "string"
)
Layers for processing the texts
text_features = text_vectorize_layer(text_input)
## Add embedding layer , dropout ...
text_features = text_vectorize_layer(text_input) # apply this "function TextVectorization layer" to text_input
text_features = layers.Embedding(size_vocabulary, output_dim = 2, name = "embedding2")(text_features) #naming it embedding 2 prevents errors
text_features = layers.Dropout(0.2)(text_features)
text_features = layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()(text_features)
text_features = layers.Dropout(0.2)(text_features)
text_features = layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(text_features)
Output layer
output = layers.Dense(2, name = "fake")(text_features)
Create the model
model2 = keras.Model(
inputs = text_input,
outputs = output
)
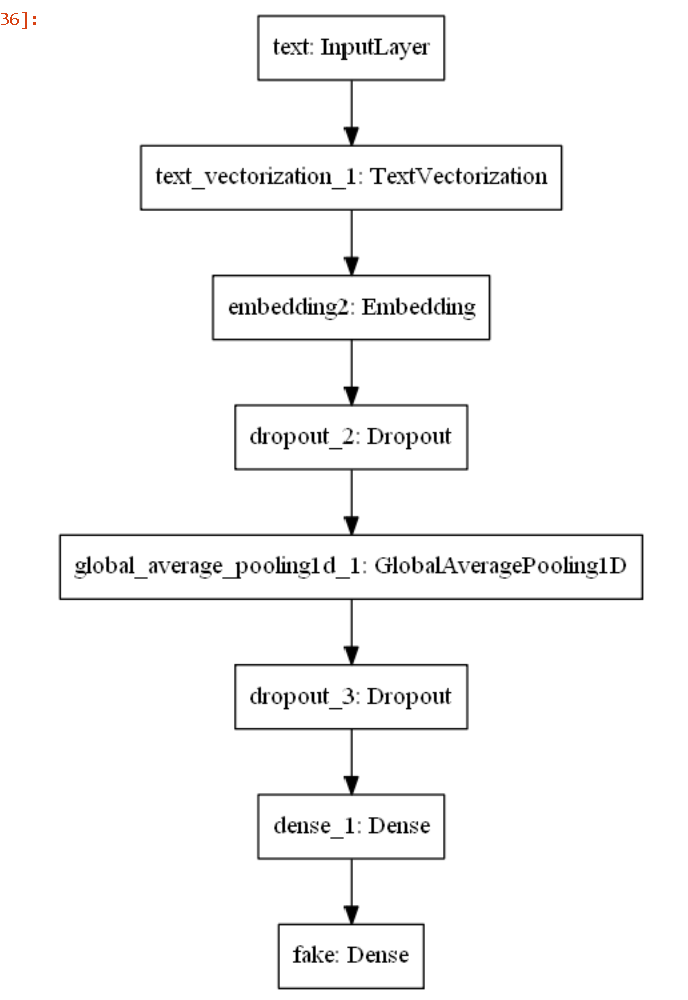
Visualize the model
keras.utils.plot_model(model2)
Compile the model
model2.compile(optimizer="adam",
loss = losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"])
Fit the model
history = model2.fit(train,
validation_data=val,
epochs = 20,
verbose = False)
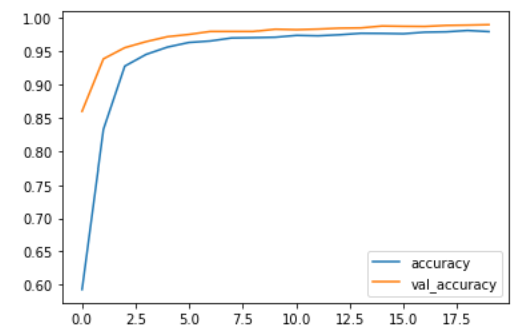
Create a plot of the model’s accuracy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history["accuracy"])
plt.plot(history.history["val_accuracy"])
Model 3 - Using article titles and text to detect fake news
In this model, both titles and texts will be used to detect fake news.
titles_features = title_vectorize_layer(titles_input) #to use for first main
text_features = text_vectorize_layer(text_input) #to use for first main
#using the two lines above will prevent a value error
main = layers.concatenate([titles_features, text_features], axis = 1)
main = layers.Embedding(size_vocabulary*2, output_dim=2, name = "embedding3")(main) #needed to implement this because with out *2, I get a value error later during embedding df
main= layers.Dense(32, activation='relu')(main)
main = layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D()(main)
main = layers.Dropout(0.2)(main)
main = layers.Dense(64, activation = 'relu')(main)
main = layers.Dense(2, name = "fake")(main)
Create the model
model3 = keras.Model(
inputs = [titles_input, text_input],
outputs = output
)
Visualize the model
keras.utils.plot_model(model3)
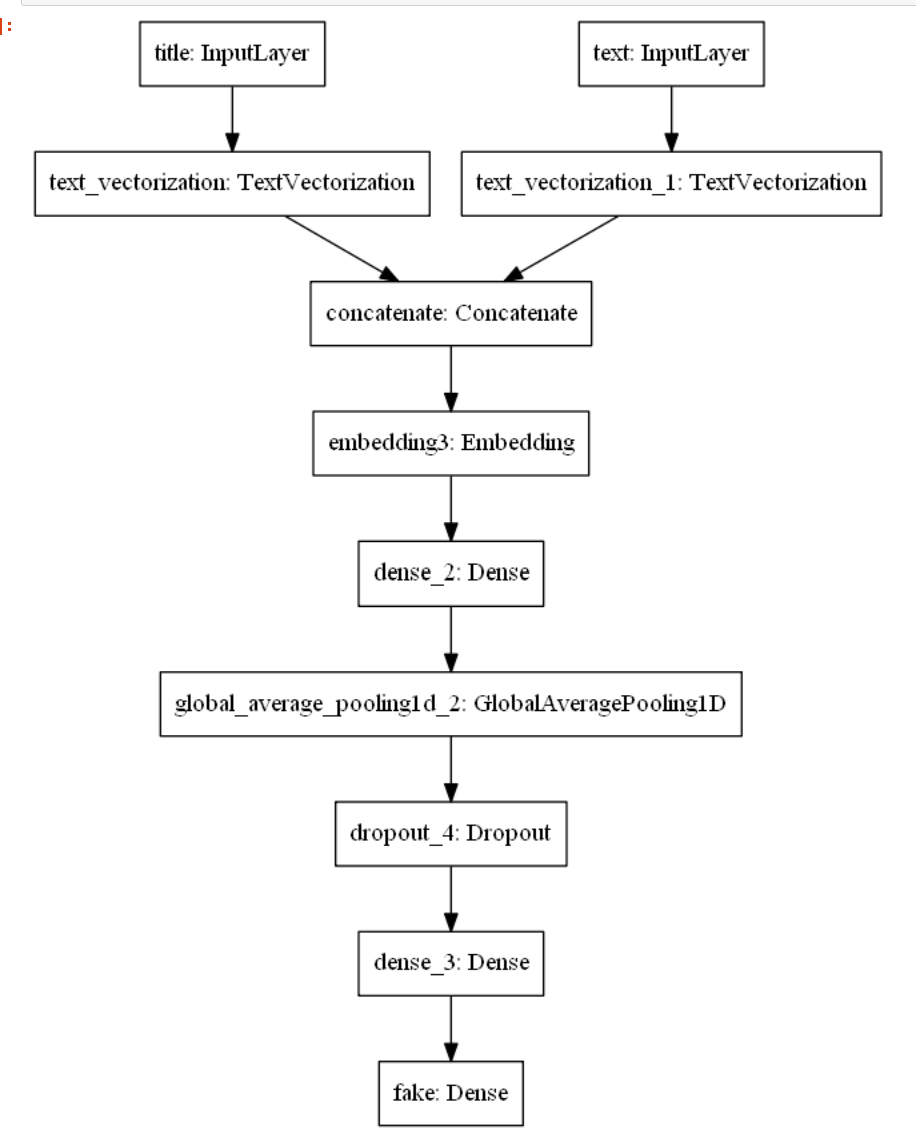
Compile the model
model3.compile(optimizer="adam",
loss = losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"])
Fit the model
history = model3.fit(train,
validation_data=val,
epochs = 20,
verbose = False)
Create a plot to visualize the model’s accuracy
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(history.history["accuracy"])
plt.plot(history.history["val_accuracy"])
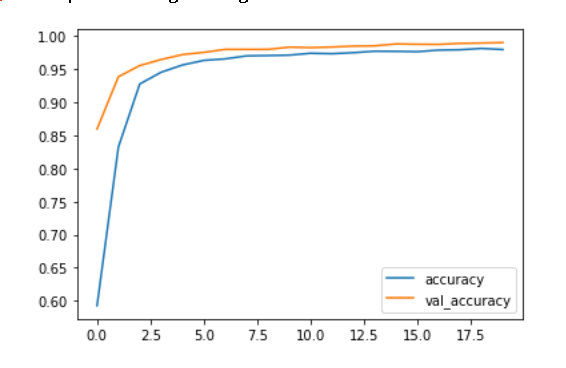
Recommendation
Based on these models’ performances, it is likely that the best algorithms use both title and text when detecting for fake news.
Model Evaluation
test_url = "https://github.com/PhilChodrow/PIC16b/blob/master/datasets/fake_news_test.csv?raw=true" #test data
testdata = pd.read_csv(train_url)
eval_test = make_dataset(testdata)
model3.evaluate(eval_test) #model performance
The accuracy was 98.86%
Word Embedding & Embedding Visualization
weights = model3.get_layer("embedding3").get_weights()[0]
vocab = title_vectorize_layer.get_vocabulary() + text_vectorize_layer.get_vocabulary() # keeps track of mapping from word to integer
#Reducing to 2D dimension
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=2)
weights = pca.fit_transform(weights)
embedding_df = pd.DataFrame({
'word': vocab,
'x0':weights[:, 0],
'x1':weights[:, 1]
})
import plotly.express as px
fig = px.scatter(embedding_df,
x = "x0",
y = "x1",
size=[2]*len(embedding_df),
hover_name = "word")
fig.show()
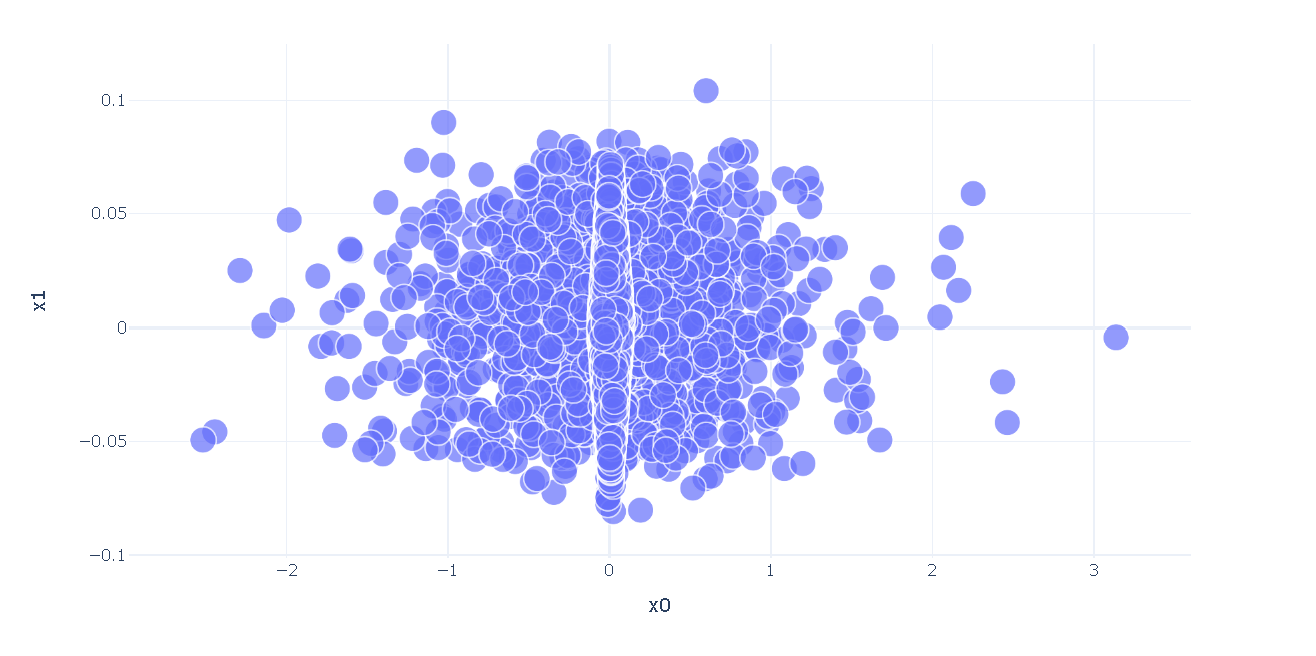
Four of the farthest left words are racism, cut, job, and viral. Perhaps this is referencing viral stories about racist motivates in the job market, but I cannot be ccertain. Some of the farthest right words are Iran, Trump, and November. Perhaps, there are stories about a November election.
